In offshore oil and gas production, an FPSO vessel is regular feature and plays a significant role in getting the crude oil out. I know that you might be interested in knowing the components of an FPSO. In this article, we look into that.
In my early years in the upstream oil and gas industry, I got very confused by the various oil and gas terms, such as FPSO or FSO.
You should know that in simple terms, a floating production storage and offloading vessel, commonly known as FPSO, is a system used to produce and store crude oil.
Since the mid-1970s about 150 FPSO’s are producing on fields in the North Sea, Brazil, West Africa, Southeast Asia, China and other locations, often in response to the need to produce in water depth beyond the reach of fixed platforms.
Floating production systems offer many advantages over permanent production platforms, often because of their operational flexibility and cost savings.
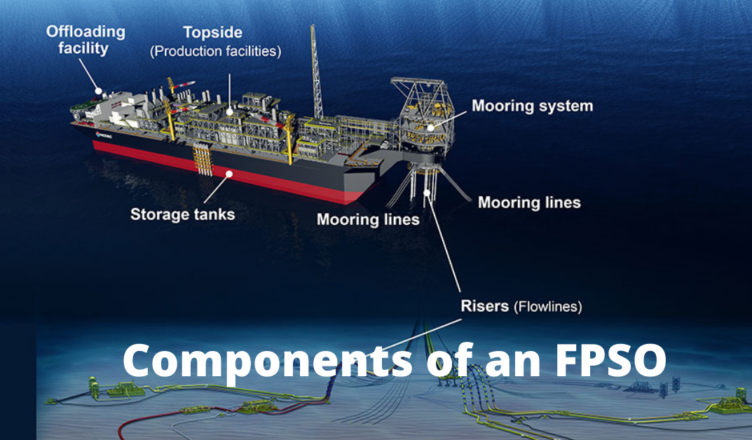
Components of an FPSO Vessel
There are several components of an FPSO that are important to proper functioning of the facility. They include;
- Spread Mooring.
- A Turret.
- Detachable FPSO Turret.
- Gas Dehydration System.
- Gas Compression System.
- Water Injection FPSO Components.
- Gas, Water and Oil Separator.
- Seawater Treatment System.
These are some of the key components or systems of an FPSO vessel. They help in ensuring that offshore production of oil and gas is taking place in a way or an environment that is secure and sustainable.
How components of an FPSO work
An FPSO vessel is designed to receive hydrocarbons produced from its wells, nearby platforms, or subsea equipment.
It has equipment on deck to process the hydrocarbons. It also stores the oil until it can be offloaded onto a shuttle tanker or, less frequently, transported through an export pipeline.
FPSOs are often the preferred concept for frontier regions where there is no local pipeline infrastructure to export oil.
A vessel used only to store oil without processing capability is referred to as a floating, storage, and offloading (FSO).
Components of an FPSO (Explained)
Here is a rundown of the core components of an FPSO vessel.
-
Spread mooring
Spread mooring is a traditional mooring system, incorporating a number of mooring lines attached to the hull of the vessel. These mooring lines are anchored onto the seabed.
-
FPSO turret (weathervaning)
The turret is integrated into the FPSOs hull, so the hull weathervanes around the mooring system and the mooring line. This enables FPSOs to position the vessel favourably against the wind so that it remains bow to wind and weather.
A turret mooring system is critical for harsh weather conditions. In essence, the turret enables the FPSO to freely rotate while moored to various locations on the seafloor.
-
Detachable FPSO turret
Many turret systems allow the turret to be disconnected from the vessel, but remain attached to the mooring lines on the seabed. This is particularly useful in situations such as hurricanes and storms, where the vessel needs to react quickly to external hazards. Once the threat has been mitigated, the FPSO can return to the turret, reattach and continue operations. This mooring system is by far the most flexible.
-
Gas Dehydration System
Gas is often saturated with water vapour, which poses a threat to facilities. Gas dehydration removes the water that is associated with natural gas.
-
Gas Compression System
Natural gas must be treated to conform to commercial standards.
-
Water injection FPSO Components
Water injection is a process where water is introduced into a reservoir to encourage oil production.
-
Gas, water and oil separator
As water, gas and oil have different densities, they can be separated with gas rising to the top, water on the bottom and oil staying in the middle. Additional debris such as sand will settle at the bottom.
-
Seawater Treatment Unit
Sea water treatment involves removing sulfates and other unwanted elements from injection water.
Benefits and Advantages of FPSO Vessel
Why have FPSOs become so important to the oil and gas companies?
Related: Advantages of an FPSO
Conceptually, FPSOs have given oil and gas companies a lot of freedom and versatility with regards to exploration and extraction. FPSOs enables companies to produce oil or gas and explore increasingly remote areas at a cheaper price in comparison to traditional offshore oil and gas production and storage methods.
Other Important Components of an FPSO
The following key components are being studied/designed by engineering companies and FPSO builders around the world:
- Process and Utilities
- Power Generation Unit
- Gas Compression and Metering Unit
- Gas Treatment Unit
- Separation Trains
- Sea Water Treatment Unit
- Produced Water Treatment Unit
- Water Injection Unit
- Chemical Treatment Unit
- Utilities
- Hull and Marine Utilities:
- Cargo
- Ballast
- Boilers
- Propulsion
- Storage
- Accommodation and Central Control Helideck
- Turret and Fluid/Control Transfer Swivel
- Moorings and Risers
FPSO vessels are particularly effective in remote or deepwater locations where seabed pipelines are not cost effective. They eliminate the need to lay expensive long-distance pipelines from the oil well to an onshore terminal.
The vessels can also be used economically in smaller oil fields that can be exhausted in a few years and do not justify the expense of installing a fixed oil platform.
Once the field is depleted, the FPSO can be moved to a new location. In areas of the world subject to cyclones, such as northwest Australia or icebergs (Canada), some FPSOs are able to release their mooring/riser turret and steam away to safety in an emergency.
The turret sinks beneath the waves and can be reconnected later.
For example, the FPSO operating at the deepest water depth is the FPSO Espirito Santo of Shell America. It is operated offshore by SBM Offshore N.V.
The FPSO is moored in water 1800 m deep in the Campos Basin in Brazil and is rated for 100,000 bpd. The EPC contract was awarded in November 2006 and was scheduled for first oil production in December 2008.
Conversions and internal turret for this FPSO vessel were done at the Keppel Shipyard in Singapore and the topsides were fabricated in modules at Dyna-Mac and BTE in Singapore.
Suppliers of Parts of an FPSO
Subsea and offshore solution providers or contractors are a major part of the supply chain. They provide or supply the various components of an FPSO.
They build the FPSO vessel, and others are supplier of parts of an FPSO.
The global floating production storage and offloading market is fairly consolidated with the presence of many large international vendors across the globe.
The top five vendors constitute approximately one-third share of the market. The major players in the market are Bumi Armada, BW Offshore, MODEC, Petrobras, and SBM Offshore.
The vendors include only the floating production storage and offloading operators.
Servicing Components of an FPSO
Floating production, storage and offloading vessels (FPSOs) are critical to any offshore oil and gas operation.
It is important that you have the right products and expertise to ensure your vessel is operating at it’s best. Therefore, servicing components of an FPSO is a major part of offshore oil and gas operations.
You have such products as lubricants from Mobil™ industrial lubricant which have proven to help extend the life of machinery, minimize downtime and extend oil service life.
When a company wins a contract to provide an FPSO vessel to an operator, the contractor signs a maintenance and servicing contract to ensure that the vessel and the components of the FPSO are In good shape during the term of the contract.
Conclusion
In conclusion, I hope you have now gotten a better understanding of FPSO and the key components of an FPSO vessel.
If you are a beginner in the oil and gas industry, this information is very important. FPSO is a terminology in the upstream oil and gas industry you should learn and know.
There are many opportunities that come with offshore oil and gas operations across the world.